|
Motor Skills
 The First Motor Skills are the Reflexes Required for Survival. The First Motor Skills are the Reflexes Required for Survival.
Ψ Reflexes that maintain oxygen supply: breathing, hiccups, sneezes, & thrashing
Ψ Reflexes that maintain constant body temperature: crying , shiver, tuck in legs, push away, & drinking
Ψ Reflexes that manage feeding: sucking, rooting, swallowing, crying, & spitting up
Ψ Other reflexes not necessary for survival but important signposts of normal development;
• Babinski reflex: occurs when the great toe flexes toward the top of the foot and the other toes fan out after the sole of the foot has been firmly stroked. This is normal in younger children, but abnormal after the age of 2.
• Stepping reflex: A reflexive movement of the leg seen in newborn infants. This lasts until about two months of age. It can be demonstrated by holding the baby in an upright position on a flat surface he or she will lift one leg in the air, then step with the other foot & "walk". Most, but not all babies exhibit this reflex.
• Primary Stepping reflex: weeks - 5 months
- If a baby is held upright on a flat surface, she will walk forward while held.
• Swimming reflex: 2 weeks - 5 months - If an infant is placed in water on his tummy, his legs & arms will move in a swimming motion.
• Palmar grasping reflex: birth - 4 months -If you touch the palm of ha bay's hand, the baby will hold onto your finger.
• Moro reflex: birth - 6 months - If a baby has a sense of falling or not being supported, the arms stretch out to the sides, & the legs stretch out full length.
• Startle reflex: 6 months - 12 months - Like the Moro Reflex, but occurs later in the baby's development.
Ψ Gross motor skills involve large body movements such as waving the arms, walking, & jumping.
Ψ Fine motor skills involve small body movements, especially with the hands & fingers.
 Age Norms (in Months) for Motor Skills Age Norms (in Months) for Motor Skills 
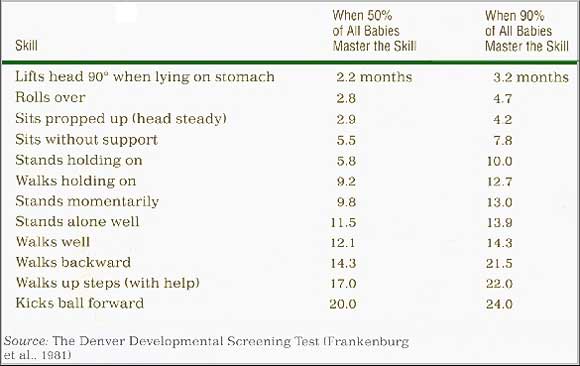
Ψ A more detailed list of the norms for movement follows:
Ψ 0-3 months
• Lies on belly & raises head
• Lies on back & moves each arm & leg equally well
• Pushes up on arms from belly & supports self on forearms
• Holds head up when held in a sitting position, with only an occasional bob forward
Ψ 4-6 months
• On belly, lifts head up to 90 degrees
• Holds head steady when upright in caregiver's arms
• On belly, pushes up onto arms, lifting chest up
• Begins to roll belly to back
• Keeps head in line with body when pulled to sitting by holding hands
• Sits with support
• Holds head up
• Sits with straight back
• Briefly sits by leaning on arms for support
Ψ 7-9 months
• Stands when held
• Sits alone
• Works to get an out-of-reach toy
• May begin to pull up on furniture
Ψ 10-12 months
• Stands holding on to someone or something
• Pulls up to standing
• Achieves a standing position
• Turns in a circle when sitting
• Walks around holding onto furniture
• May stand alone momentarily
• Crawls on hands & knees
Ψ 12-18 months
• Walks or stands independently
• Walks upstairs with help
• Throws from standing without falling
• Throws ball towards you
• Attempts to kick a large ball
• Rolls ball to you
|























