Note: These questions are part of a larger data base of questions & are selected to represent the type of question you should expect on unit exams . Exam questions, however, may deal with topics not covered in the self tests or in lectures but are discussed in your textbook. You are responsible for the content of your text book plus the content of lectures, interactive activities, & material on the web site.Use these sample questions to test yourself & to practice for the test. Click on your choice to see if you are right.1. Which of the following is not a characteristic of all senses?
• adaptation
|
5. The path that light takes through your eye is
• cornea; pupil; lens; retina.
|
|
6. You detect the strong smell of cedar when you enter a furniture store. However, after a short while in the store you can no longer detect the smell. This process is know as
• sensory adaptation.
• habituation.
• perceptual constancy.
• accommodation.
7. Which of the following terms refers to the amplitude of a light wave such as how high or low the wave is?
• color
• brightness
• pitch
• hue
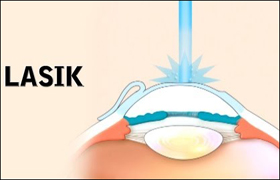
8. When an ophthalmologist surgically corrects a patient's vision through LASIK or PRK, the doctor is making adjustments to the patient's
• cornea.
|
|
9. The trichromatic theory explains how
• we experience an afterimage.
• cones in the retina change light waves into colors.
• rods in the retina change light waves into colors.
• the brain changes light waves into color.
10. What part of the eye hardens as we age thus causing many to suffer from presbyopia?
• rods
• cones
• lens
• vitreous humor
11. A deer's inability to quickly respond to the headlights of an approaching car is due to what sensory phenomenon?
• dark adaptation
|
|
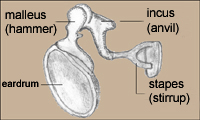
12. Which of the following cliches best describes the relationship between the hammer, anvil, and stirrup?
• Passing the buck
• Out of sight, out of mind
• A stitch in time saves nine
• A penny saved is a penny earned
13. The hammer, the anvil, and the stirrup are
|
|
14. John has played his music loudly for years. Now, in his 20s, he finds he has a continuous ringing in both of his ears. What would John probably be diagnosed with?
• Tinnitus, which is a nerve based disorder that has no permanent cure.
• Conduction-based hearing impairment; however, hearing aids may be able to help.
• Damage to the pinna, which can be corrected with surgery.
• Regardless of the disorder, John will ultimately require a cochlea inplant.
15. Studies show that taste preference can typically begin
• before the baby is born.
• in the first 3-6 months after birth.
• by age 1.
• during preschool.
16. If we could state flavor in a mathematical formula, what would it look like?
• taste = flavor
• taste + spicy = flavor
• taste + smell = flavor
• bitter + sour + salty + sweet = flavor
17. John has been suffering from a serve cold. His nose has been stopped up for several days. What effect, if any, might his cold have on his sense of taste?
• His sense of taste will be increased since he isn't receiving additional sensory
input from his smell.
• His sense of taste will be dulled since taste and smell often work together.
• His sense of taste will get better but not until 48 hours after he losses his
sense of smell.
• His sense of taste will be no better or worse since the senses of taste and smell
are completely separate.
18. If a child suffers from congenital analgesia, why must he or she be careful when playing outside?
• The child cannot hear sounds unless he or she is within 3 feet of the source.
• The child cannot feel pain and can suffer injuries without ever noticing it.
• The child lacks the ability to react to a dangerous situation.
• The child's sense of smell does not work properly.
19. If Tabitha closes her eyes when she rides in her parent's car, she can still tell that the car is moving. This is due to the movement of tiny crystals in the
• outer ear.
• cochlea.
• otolith organs.
• middle ear.
20. A child sometimes may play by quickly turning around in a circle. When the child stops, he or she often feels like his or her head is still spinning. What is responsible for this sensation?
• fluid still rotating in the semicircular canals
• proprioceptors
• compression of the otolith organs
• disruptions of the otolith organs
21. What is the fifth taste that we can detect?
• umami
• flowery
• rancid
• acidity
22. Our sense of touch comes from
• a half-dozen miniature sensors located in the skin.
• special glands for pressure, temperature, and pain.
• stimulation of the tiny hairs that cover the body.
• millions of tiny nerves on the surface of the skin.
23. Little Karla is with her mother at the docks waiting for her daddy to return from his naval deployment. While the boat is still always out, her mother says, "there is daddy's boat:. Karla is confused. She cannot understand how her dad can be on a boat that is so small that she can hold up her thumb and the boat disappears. It's safe to assume that Karla does not yet understand
• size constancy.
• shape constancy.
• brightness constancy.
• color constancy.
24. XX XX XX XXXXXX
XX XX XX XXXXXX
XX XX XX XXXXXX
In viewing the items above, seeing three columns of Xs on the left versus three rows of Xs on the right can be explained by the Gestalt principle of __________.
• closure
• similarity
• proximity
• contiguity
25. Illusions
• correspond directly to reality.
• are the same thing as hallucinations.
• exist only in the brain cells of the viewer.
• are a distorted perception of the actual stimuli.
26. From past experience, you know that commercial jets typically fly around 500 miles per hour at a height of 30,000 feet. However, as you watch one fly overhead, it seems to slowly pass by. What monocular depth cue best explains this?
• motion parallax
• linear perspective
• overlap
• texture gradient
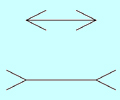
27. The Muller-Lyer illusion is influenced greatly by
• age.
|
|
28. Allison opened her new jigsaw puzzle but soon realized that she had the same puzzle when she was a child. With her past experience to rely on, Alison will probably use ___________ to help her reassemble the puzzle.
• bottom-up processing
• top-down processing
• perceptual expectancy
• perceptual set
29. The perceptual set
• involves the characteristics of the perceiver, or what is being perceived under what conditions.
• includes motivation, context, emotional state, past experience and cultural background.
• refers to the setting or environment in which a perception is made.
• is the predisposition or 'readiness' to perceive something in accordance with what
we expect it to be. Our expectations of what an object or event will be make us
more likely to interpret the object or event in the predetermined way.
30. Kip enjoys playing with sparklers on the 4th of July. He always loves watching a friend run with the sparkler and the momentary trail of light that seems to be left behind. Which aspect of our visual system best explains this trail of light?
• lateral inhibition
• microsaccades of the eyes
• persistence of vision
• achromatopsia
31. The process by which lower centers of the brain “ignore” or prevent conscious attention to stimuli that do not change is called
• sensory adaptation.
• habituation.
•
sensation.
• subliminal perception.
• absolute threshold.
32. The ___________________ theory proposes that the combination of red, blue, and green cones and rate at which they fire determines what color will be seen.
• opponent-process theory
• trichromatic theory
• light adaptation
• dark adaptation
• afterimage theory
33. One monocular cue that can be used to perceive depth in which parallel lines appear to converge as they become further away in distance (as with railroad tracks) is called
• relative size.
• texture gradient.
• aerial perspective.
• linear perspective.
• motion parallax.
34. The tendency for people to assume that a blocked object is behind another object, and is therefore further away, is called
• interposition.
• accommodation.
• binocular disparity.
• convergence.
• relative size.
35. This Gestalt principle explains why we tend to group items that are close together in time as being related.
• Closure
• Similarity
• Proximity
• Continuity
• Contiguity
36. Ned found a decaying carcass lying on the beach. Looking at the size of it he decided that it was like the Loc Ness monster. Ned likes to read about mythical animals. We might expect that he has made an error of perception due to
• perceptual set.
• bottom-up processing.
• perceptual defense.
• cognitive convergence.
37. What is the process called in which one form of energy is changed into another. In sensation, the transforming of stimulus energies, such as touch and smells, into neural impulses our brain can interpret?
• Priming
• Transduction
• Sensation
• Sensory Adaption
38. If a stimulus is below the absolute threshold it is said to be?
• Sublingual
• Not of importance
• Subliminal
• None of the Above
39. The process by which our brains organize and interpret sensory information, sorting it into useful information is?
• Sensation
• Perception
• Subliminal
• None of the above
40. Which of the following are monocular cues?
• Light and Shadow
• Linear Perspective
• Interposition
• Relative Size
• All of the above
• Print Friendly Version
|
General Psychology Robert C. Gates 
|
|