|
Ψ Social Sources of Prejudice:
• Unequal status & prejudice
• The self-fulfilling prophecy: where a belief (often false) is accepted as truth, & in stating it, becomes true.
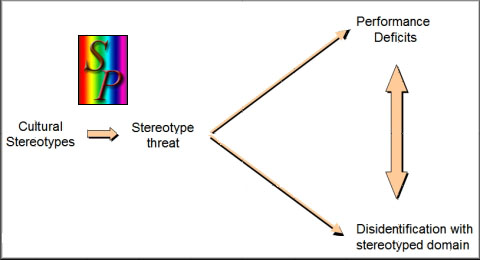
• Stereotype threat is "the threat of being viewed through the lens of a negative stereotype, or the fear of doing something that would inadvertently confirm that stereotype," such as the stereotype that women perform poorly in math. Steele explains that some students try to escape stereotype threat by disidentifying with the part of life in which the stereotype originates, such as race or ethnic identities. The article defines what an academic community can do to reduce or completely eliminate stereotype threat - increase the degree of racial trust, or the assurance of racial fairness in assessment. From: "Thin Ice: 'Stereotype Threat' and Black College Students," by Claude M. Steele, The Atlantic Monthly
http://www.theatlantic.com/issues/99aug/9908stereotype.htm
Ψ Social Identity
• Social Identity Theory: proposes that the membership of social groups & categories forms an important part of our self concept.
• We categorize all groups.
• We identify (associate) with ingroups.
• We compare our
social group with outgroups.
• Ingroup bias is the preferential treatment people give to whom they perceive to be members of their own groups.
• Conformity: Once established, prejudice is maintained
largely by inertia. If prejudice is socially accepted, most will follow the path of least resistance & conform to fashion. If prejudice is nor deeply ingrained in personality, then as fashions change & new norms evolve, prejudice will diminish.
Ψ Emotional Sources of Prejudice:
• Frustration & aggression:
• The Scapegoat Theory: When problems occur, people do not like to blame themselves. They will thus actively seek scapegoats onto whom they can displace their aggression. Scapegoats may be out-group individuals or even entire groups. Powerless people who cannot easily resist will often become victims of scapegoatimg. Scapegoating increases when people are frustrated & seeking an outlet for their anger.
|

|
• The Realistic Group Conflict Theory: When there are limited resources, then this leads to conflict, prejudice & discrimination between groups who seek that common resource,
• Personality dynamics
• Need for status, self-regard, & belonging
• The Authoritarian Personality
• Ethnocentricity: Holding the belief that one's own cultural tradition or racial group is superior to all others.
Ψ Cognitive Sources of Prejudice
• Categorization: We stereotype when
• Pressed for time
• Preoccupied
• Tired
• Emotionally aroused
• Too young to appreciate diversity
• Categorization: Perceived similarities & differences
• Outgroup homogeneity effect: The tendency to perceive out-group members as "they are all alike" compared to the in-group is called the out-group homogeneity effect. We do see diversity in our own group.
• Distinctiveness: Distinctive people & vivid or extreme
occurrences often capture attention & distort judgments. This sometimes breeds stereotypes.
• Attribution: The just-world phenomenon, refers to the tendency for people to believe that the world is "just" & so therefore people "get what they deserve." It wrongly colors our impression of "victims" of any sort.
Social Psychology
Robert C. Gates
|

|
|













