|
|
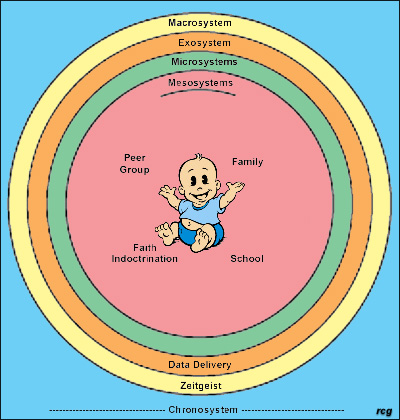
The Ecological ModelΨ The influences within & between the systems or contexts in the model are multidirectional & interactive. |
|
The Ecological Perspective (Urie Bronfenbenner)
• Focus is on an individual’s relationship within his/her social contexts.
• Human development occurs in a set of overlapping ecological systems.
• The ecological systems operate together to influence what a person becomes as they develop.
Microsystems Defined
• Immediate social settings which an individual is involved in.
• Focus is on an individuals face-to-face interaction (Family, school, work, church, peer group)
• Activities & interaction patterns in child's immediate surroundings. (e.g., parent/family in the home; teachers, peers in school or day care)
Mesosystem Defined
• Links 2 Microsystems together, directly or indirectly.
• e.g when parents and teachers coordinate their efforts to educate a child.
• Connections among children's immediate settings. (e.g., Relationship between parent & teacher in settings such as day care, schools, neighborhoods)
Exosystem Defined
• Settings in which the person does not actively participate but in which significant decisions are made affecting the individuals who do interact directly with the person.
• (e.g. – neighborhood/community structures that affect the functioning of smaller systems: newspapers, TV, & radio.
• Child not directly involved in social setting; Involves connection to broader community (e.g., Parents' social networks; effect of workplace policies on day care arrangements)
Marcosystem Defined
• Plans for defining and organizing the institutional life of the society, including overarching patterns of culture, politics, economy, etc.
• Values, laws, customs, resources of culture, society; Influences experience & interaction at inner layers
Chronosystem Defined
• Environment is an ever-changing system.
• Invoves temporal (time-related) experiences.
• Indicates that History influences Microsystems & all subsequent layers.
Ψ Urie Bronfenbrenner's (1917- 2005) ideas & his ability to translate them into operational research models & effective social policies spurred the creation in 1965 of Head Start, the federal child development program for low-income children & their families. In 1979 Bronfenbrenner further developed his thinking into the groundbreaking theory on the ecology of human development. That theoretical model transformed the way many social & behavioral scientists approached the study of human beings & their environments. It led to new directions in basic research & to applications in the design of programs & policies affecting the well-being of children & families both in the United States & abroad.
|
Growth & Development Robert C. Gates 
|